|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| {{MitoPedia | | {{MitoPedia |
| |application=O2
| |
| |abbr=FNSGp(Oct,PGM) | | |abbr=FNSGp(Oct,PGM) |
| |description=[[File:1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot-.png|400px]] | | |description=[[File:1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot-.png|400px]] |
| |SUIT number=D05_1D;2M;3Oct;3c;4M;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama;12AsTm;13Azd | | |SUIT number=D05_1D;2M;3Oct;3c;4M;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama;12AsTm;13Azd |
| |info='''A: RP2''' - [[SUIT-002]] | | |info='''A: RP2''' - [[SUIT-002]] |
| }}
| | |application=O2 |
| {{MitoPedia concepts
| |
| |mitopedia concept=SUIT protocol | |
| }} | | }} |
| ::: [[MitoPedia: SUIT]] - '''[[SUIT reference protocol]] RP2''' | | ::: [[MitoPedia: SUIT]] - '''[[SUIT reference protocol]] RP2''' |
| ::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols|SUIT-category]]:''' FNSGp(Oct,PGM) | | ::: '''[[Categories of SUIT protocols|SUIT-category]]:''' FNSGp(Oct,PGM) |
| ::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' diametral | | ::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' diametral 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot |
|
| |
|
| == References == | | == References == |
| Line 27: |
Line 24: |
|
| |
|
| {{Template:SUIT-002}} | | {{Template:SUIT-002}} |
| | |
| | {{MitoPedia concepts |
| | |mitopedia concept=SUIT protocol |
| | }} |
| | {{MitoPedia methods |
| | |mitopedia method=Respirometry |
| | }} |
Revision as of 10:27, 15 January 2019

- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
SUIT-002 O2 mt D005
Description
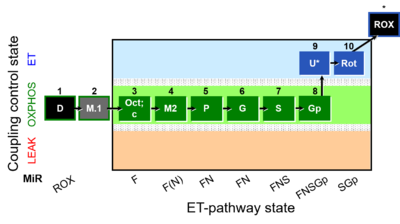
Abbreviation: FNSGp(Oct,PGM)
Reference: A: RP2 - SUIT-002
SUIT number: D05_1D;2M;3Oct;3c;4M;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama;12AsTm;13Azd
O2k-Application: O2
- MitoPedia: SUIT - SUIT reference protocol RP2
- SUIT-category: FNSGp(Oct,PGM)
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot
References
Steps and respiratory states
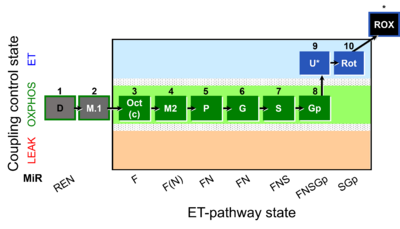
| Step
|
State
|
Pathway
|
Q-junction
|
Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
| 1D
|
REN
|
|
|
1D
- ADP is added to stimulate the consumption of endogenous fuel-substrates.
|
| 2M.1
|
|
|
|
1D;2M.1
|
| 3Oct
|
OctMP
|
F
|
FAO
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration.
|
| 3c
|
OctMcP
|
F
|
FAO
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
- Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM (cytochrome c control efficiency). Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in the preceding state without added c due to loss of cytochrome c. Typically, cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step (OXPHOS capacity P with saturating [ADP]).
|
| 4M2
|
OctMP
|
F(N)
|
FAO
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid FA in the presence of malate M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. In the presence of anaplerotic pathways (e.g., mitochondrial malic enzyme, mtME) the F-pathway capacity is overestimated, if there is an added contribution of NADH-linked respiration, F(N) (see SUIT-002). The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the FAO-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration.
- High concentration of malate, typically 2 mM, saturates the N-pathway.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 5P
|
OctPMP
|
FN
|
FAO&CI
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 6G
|
OctPGMP
|
FN
|
FAO&CI
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 7S
|
OctPGMSP
|
FNS
|
FAO&CI&II
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway, N-pathway, and S-pathway, with convergent electron flow in the FNS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function and additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 8Gp
|
OctPGMSGpP
|
FNSGp
|
FAO&CI&II&GpDH
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp
|
| 9U
|
OctPGMSGpE
|
FNSGp
|
FAO&CI&II&GpDH
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U
|
| 10Rot
|
SGpE
|
SGp
|
CII&GpDH
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot
- Respiratory stimulation by action of succinate and glycerophosphate, Gp, with convergent electron flow in the SGp-pathway (CII&GpDH-linked pathway to the Q-junction).
- Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E.
|
| 11Ama
|
ROX
|
|
|
1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama
- Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of CIII). Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration (mt).
|

- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- » Coupling control state
- » ET capacity
- » OXPHOS capacity
- » LEAK respiration
- Pathway control
- » Electron transfer pathway
- » Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state, F
- » NADH electron transfer-pathway state, N
- » Succinate pathway control state, S
- » NS-pathway control state, NS
- » Glycerophosphate pathway control state, Gp
- » Complex IV single step, CIV
- » Anaplerotic pathway control state
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Glossary
- » List of SUIT states
- » SUIT concept
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT protocol
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry



