Description
GMS: Glutamate & Malate & Succinate.
MitoPathway control: CI&II
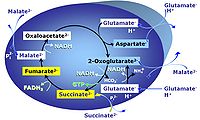
Transaminase catalyzes the reaction from oxaloacetate to 2-oxoglutarate, which then establishes a cycle without generation of citrate. OXPHOS is higher with GS (CI&II) compared to GM (CI) or SRot (CII). This documents an additive effect of convergent CI&II electron flow to the Q-junction, with consistent results obtained with permeabilized muscle fibres and isolated mitochondria (Gnaiger 2009).
Abbreviation: GMS
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 5.5
MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry: "SUIT state" is not in the list (O2k hardware, DatLab, Oroboros QM, O2k-Open Support, O2k-Respirometry, O2k-FluoRespirometry) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry" property.
SUIT state"SUIT state" is not in the list (O2k hardware, DatLab, Oroboros QM, O2k-Open Support, O2k-Respirometry, O2k-FluoRespirometry) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry" property.
GMS(L)
GMS(P)
GMS(E)
Discussion
In human skeletal muscle mitochondria (25 °C), Rasmussen and Rasmussen (2000) obtained CI/CI&II flux ratios of 0.7 (0.6) for OXPHOS (or ETS) with glutamate&malate (8+4 mM) and glutamate&succinate (4+8 mM), and CII/CI&II flux ratios of 0.8 (0.6) for OXPHOS (or ETS). The GMP/GMSE and S(Rot)E/GMSE flux control ratios are 0.50 and 0.55 in human vastus lateralis (Pesta et al 2011). Due to the lower H+/O2 stoichiometry in succinate respiration compared to CI-linked respiration (two versus three coupling sites), the CI/CI&II ratio is lower for LEAK respiration (0.3 to 0.4; Garait et al 2005) compared to OXPHOS capacity. In human skeletal muscle, the phosphorylation system is more limiting at the highest OXPHOS activity with glutamate&succinate, at a P/E ratio (GSP/GSE) of 0.69 versus 0.80 with glutamate&malate (Rasmussen and Rasmussen 2000). Failure of obtaining a further stimulation of coupled OXPHOS in human skeletal muscle mitochondria with GMS by uncoupling (Kunz et al 2000) can be explained by the high FCCP concentration applied (10 µM) which is known to inhibit respiration (Steinlechner-Maran et al 1996). In mouse skeletal muscle, however, the P/E ratio is actually 1.0 (Aragones et al 2008), which contrasts with the significant limitation of OXPHOS capacity by the phosphorylation system in humans