Esterhazy 2008 Biochemistry
| Esterházy D, King MS, Yakovlev G, Hirst J (2008) Production of reactive oxygen species by complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) from Escherichia coli and comparison to the enzyme from mitochondria. Biochemistry 47:3964-71. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi702243b |
Esterházy D, King MS, Yakovlev G, Hirst J (2008) Biochemistry
Abstract: The generation of reactive oxygen species by mitochondrial complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) is considered a significant cause of cellular oxidative stress, linked to neuromuscular diseases and aging. Defining its mechanism is important for the formulation of causative connections between complex I defects and pathological effects. Oxygen is probably reduced at two sites in complex I, one associated with NADH oxidation in the mitochondrial matrix and the other associated with ubiquinone reduction in the membrane. Here, we study complex I from Escherichia coli, exploiting similarities and differences in the bacterial and mitochondrial enzymes to extend our knowledge of O2 reduction at the active site for NADH oxidation. E. coli and bovine complex I reduce O2 at essentially the same rate, with the same potential dependence (set by the NAD (+)/NADH ratio), showing that the rate-determining step is conserved. The potential dependent rate of H2O2 production does not correlate to the potential of the distal [2Fe-2S] cluster N1a in E. coli complex I, excluding it as the point of O2 reduction. Therefore, our results confirm previous proposals that O2 reacts with the fully reduced flavin mononucleotide. Assays for superoxide production by E. coli complex I were prone to artifacts, but dihydroethidium reduction showed that, upon reducing O2, it produces approximately 20% superoxide and 80% H2O2. In contrast, bovine complex I produces 95% superoxide. The results are consistent with (but do not prove) a specific role for cluster N1a in determining the outcome of O2 reduction; possible reaction mechanisms are discussed.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
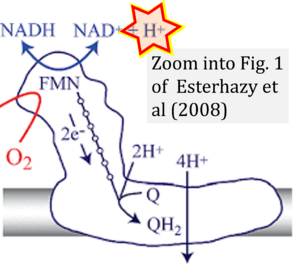
Hydrogen ion ambiguities in the electron transfer system
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2023-10-08) last update 2023-11-10
- Electron (e-) transfer linked to hydrogen ion (hydron; H+) transfer is a fundamental concept in the field of bioenergetics, critical for understanding redox-coupled energy transformations.
- However, the current literature contains inconsistencies regarding H+ formation on the negative side of bioenergetic membranes, such as the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane, when NADH is oxidized during oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Ambiguities arise when examining the oxidation of NADH by respiratory Complex I or succinate by Complex II.
- Oxidation of NADH or succinate involves a two-electron transfer of 2{H++e-} to FMN or FAD, respectively. Figures indicating a single electron e- transferred from NADH or succinate lack accuracy.
- The oxidized NAD+ is distinguished from NAD indicating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide independent of oxidation state.
- NADH + H+ → NAD+ +2{H++e-} is the oxidation half-reaction in this H+-linked electron transfer represented as 2{H++e-} (Gnaiger 2023). Putative H+ formation shown as NADH → NAD+ + H+ conflicts with chemiosmotic coupling stoichiometries between H+ translocation across the coupling membrane and electron transfer to oxygen. Ensuring clarity in this complex field is imperative to tackle the apparent ambiguity crisis and prevent confusion, particularly in light of the increasing number of interdisciplinary publications on bioenergetics concerning diagnostic and clinical applications of OXPHOS analysis.